Bumblebee stings
Two of the main reasons for using bumblebees for pollination is that they are more docile and less aggressive than bees. However, even with a proper handling of the hive, you could be stung by a bumblebee.
Only female bumblebees (workers and queens) have a stinger. Thus, only female bumblebees are able to sting. The bumblebee’s stinger, as well as the wasp’s stinger, is smooth and retractable, so they can sting multiple times. On the other hand, the bee’s stinger, which is jagged and hook shaped, gets stuck in the skin when they sting.

Bumblebees only sting if they feel threatened or their colony is under attack. To reduce the risk of being stung when working with our hives, try to keep calm and follow the advices below:
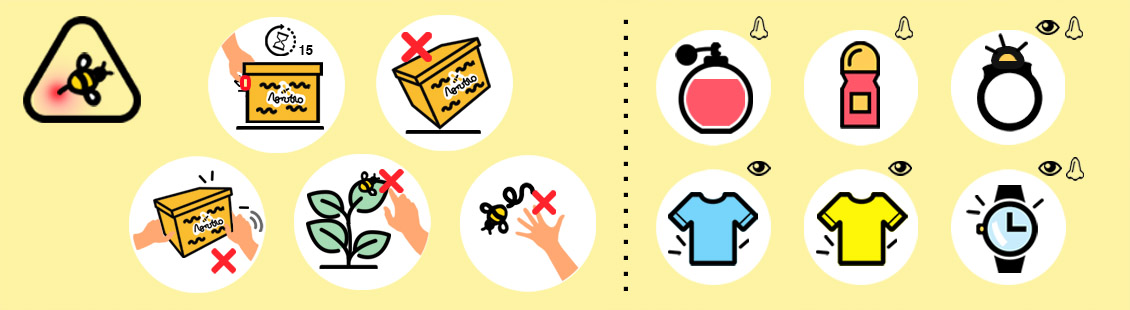
- Do not open the hive until the colony of bumblebees is calm.
- Do not make the bumblebees to feel threatened or disturbed: do not hit the hive, do not hold it…
- Avoid sudden movements: wild gesticulations, slaps, strong breathing…
- Avoid wearing baggy or vivid colour clothes.
- Wear long trousers and long sleeve shirts, as well as shoes with long socks.
- Be careful with strong smells: sweat, alcohol, perfume, soap…
- Avoid wearing bright accessories: rings, watches, bracelets…
TYPES OF REACTIONS AND TREATMENTS
Bumblebees inject a small quantity of poison through their stinger. The allergic reactions are variable and depend on the affected zone, as well as the person’s sensitivity. In general, the types of reactions are:
- Local reactions: It is the skin reaction to a sting. Inflammation (sometimes more than 10 cm diameter), reddening, pain during the first minutes and later, a stinging sensation. The inflammation and stinging can last for hours or even days. These reactions only need to keep the sting area clean, with water and soap; and to apply cold locally in order to reduce the inflammation and pain. Stings in more sensitive zones may require the use of antihistamines and/or corticoids, always under medical prescription. If the sting is near to your neck or mouth, it could block your respiratory track, so you should go immediately to the nearest emergency medical service.
- Generalized reactions: These are more important allergic reactions, characterised by stinging and rash distant from the sting zone or in the whole body and, sometimes, difficulty to breath, drop of blood pressure or alteration of the level of consciousness. These reactions require a medical treatment but, above all, keep calm; otherwise the reaction will get worse. Go to your nearest hospital or healthcare centre as soon as possible. If the symptoms are serious, contact your emergency medical service and follow the instructions given by specialised personnel.


